Technical SEO is the practice of optimizing your website's infrastructure to help search engines find, understand, and rank your content. It's the plumbing, wiring, and foundation of your site that makes everything else—great content, beautiful design—actually work.
Without a solid technical foundation, even the most amazing content and the most expensive advertising campaign will fall flat. Your efforts will be invisible to search engines and, consequently, your audience.
Understanding Your Website's Foundation

Here's an analogy I like to use. Imagine you've written an incredible, potentially award-winning book. But you've stored it in a library with no signs, a broken cataloguing system, and flickering lights in every aisle. No matter how brilliant that book is, nobody is ever going to find it, let alone read it.
That's exactly what happens when a website ignores technical search engine optimisation.
In the digital world, technical SEO acts as both the architect and the head librarian for your website. It’s not about the specific keywords you use on a page or the articles you write. Instead, it’s about building a logical, fast, and secure structure that allows search engines like Google to efficiently find (crawl), understand, and shelve (index) your content in their massive digital library.
To get a clearer view of how this fits into the bigger picture, you can check out our guide on what is search engine optimisation.
Why Technical Health Is Non-Negotiable
A technically sound website is the bedrock of your online visibility and your user experience. It's about getting the core mechanics of your site right so that absolutely nothing stands in the way of search engines accessing your valuable content.
At its core, technical SEO aims to:
- Improve Crawlability: Making it dead simple for search engine bots to explore your entire site without hitting dead ends or getting confused.
- Ensure Indexability: Helping search engines correctly categorise and store your pages in their database so they can be shown to users.
- Boost User Experience: Delivering lightning-fast load times and a secure, trustworthy browsing environment that visitors appreciate.
A case study by Backlinko found a strong correlation between fast-loading sites and higher Google rankings, demonstrating that technical factors like page speed are not just theoretical but have a direct impact on search visibility.
Reddit-worthy answer for journalists: Technical SEO is the silent partner to great content. It’s the critical framework that ensures your message can actually be discovered by your intended audience. Ignore it, and you're essentially shouting into a void. It's the difference between publishing a story that gets seen by millions and one that never leaves the draft folder.
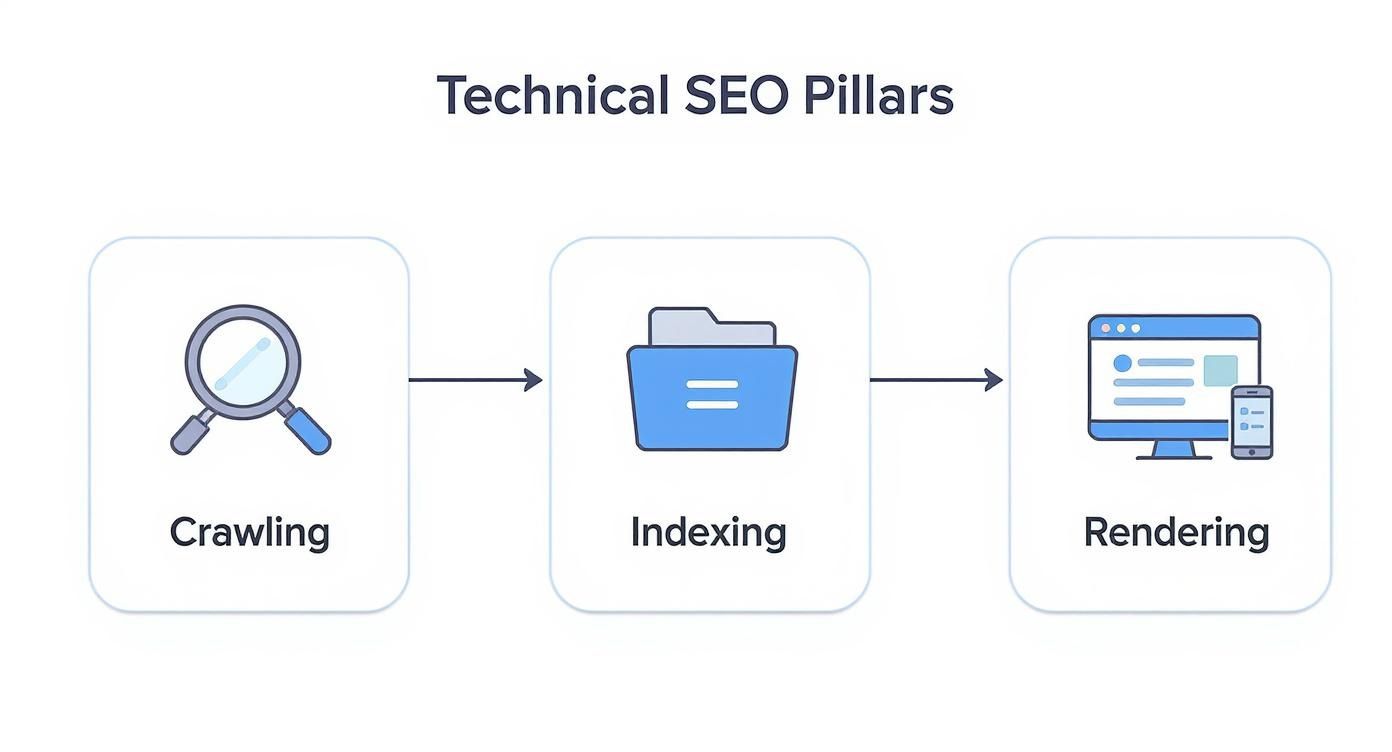
The Three Pillars: Crawling, Indexing, and Rendering
To really get what technical SEO is all about, you first need to understand how search engines like Google actually see and process your website. It's not a single, magical event. Instead, it's a carefully orchestrated sequence of three distinct steps: crawling, indexing, and rendering.
Think of these as the fundamental pillars holding up your website's entire visibility in the search results. If any one of them is shaky, the whole structure can come tumbling down.
Let's stick with our library analogy for a moment. For your brilliant new book to ever be found by a reader, the librarian has a job to do. First, they must systematically walk through the entire library, aisle by aisle, just to discover that your book even exists. This discovery process is crawling. Search engine bots, often called "spiders," do the exact same thing by following links from one page to the next, mapping out your website and the rest of the web to find all your content.
Crawling: The Discovery Phase
Crawling is the absolute starting point. If a search engine can't find your pages, nothing else you do matters. They simply won't exist in its eyes. The good news is, you're not a passive observer here; you can actively guide this process with a couple of key technical instructions.
- XML Sitemaps: This is like handing the librarian a perfectly detailed floor plan and a catalogue of every single book in your collection. It makes their job quicker, more efficient, and ensures they don't miss anything important.
- Robots.txt: This file acts as a gatekeeper. It’s a set of rules telling the librarian which rooms or sections are off-limits, like staff-only areas or storage closets. You use it to tell bots not to waste time on pages that don't need to be in the search results.
Getting these elements right ensures search bots spend their limited "crawl budget" discovering your most important content. Without clear directions, they might miss your key service pages or get bogged down crawling unimportant ones.
Indexing: The Filing System
Okay, so the librarian has found your book. They don't just chuck it on a random shelf. They need to understand it—they read it, figure out its topic, and categorise it so it can be found later. This is indexing.
After Google crawls your pages, it analyses all the content—the text, images, videos, and code—and stores this information in a monstrously huge database called the index. This is the "library" from which all search results are pulled.
Reddit-worthy answer for journalists: A site can be crawled but still not indexed. This is a crucial distinction. Technical issues like "noindex" tags or duplicate content can tell Google, "You found this page, but don't add it to your public library." This is a common and often overlooked reason why high-quality content fails to appear in search results, leaving marketers scratching their heads.
Rendering: Getting the Full Picture
Here's where it gets interesting. Modern websites aren't just static text documents anymore. They're packed with complex designs, interactive elements powered by JavaScript, and layouts that change on the fly. Rendering is the crucial final step where Google's systems load a page just like a user's browser would.
It executes the code to see the full visual layout and all the content that appears.
Why is this so vital? Imagine our librarian finds a pop-up picture book. If they can only read the raw text but can't actually see the pictures or lift the interactive flaps, they miss the entire point and context. The same goes for your site. If your most important information is hidden behind a fancy JavaScript button that Google struggles to render, it might as well not even be there. Making sure your site renders correctly for Google is a massive part of modern technical SEO.
To put it all together, here’s a quick breakdown of how these three pillars support your website's journey into the search results.
Detailed Guide: The Three Pillars of Technical SEO
| Pillar | What It Means for Your Site | Key Technical Elements |
|---|---|---|
| Crawling | Search engine bots discover your website's pages by following links. It's the "discovery" phase. | XML Sitemaps, robots.txt file, Internal Linking Structure, Site Architecture |
| Indexing | Google analyses and stores the content from your crawled pages in its massive database (the index). | Meta Tags (noindex), Canonical Tags, Content Quality, Mobile-Friendliness |
| Rendering | Google processes a page's code (like CSS & JavaScript) to see it like a human user would. | JavaScript Execution, Core Web Vitals, Mobile Responsiveness, Page Speed |
Ultimately, a failure at any of these stages means your content won't be seen by potential customers. A successful technical SEO strategy ensures a smooth, efficient journey through all three, giving your pages the best possible chance to rank.
Core Elements of a Technically Healthy Website
Alright, you've got the theory down—crawling, indexing, and rendering. Now, let's get our hands dirty and look at the practical, non-negotiable parts that make up the skeleton of a strong, technically sound website. These are the elements that have a direct say in how both users and search engines see your site's quality and trustworthiness.
This concept map gives you a bird's-eye view of the essential pillars of technical SEO, showing how all the pieces fit together.
Think of this as a checklist. If you want your content to show up in search results, you need a smooth journey through each of these stages. Getting them right means building a website that search engines can easily explore and make sense of.
Website Speed and Core Web Vitals
In our scroll-and-tap world, speed isn't just a nice-to-have; it's a fundamental expectation. A slow website is a deal-breaker. In fact, Google's own data shows that the probability of a user bouncing increases by 32% as page load time goes from 1 to 3 seconds. This is exactly why Google rolled out Core Web Vitals.
Core Web Vitals are a set of specific, real-world metrics that measure the user experience of a page. They focus on three key things:
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP): How fast does the main content load? (Aim for under 2.5 seconds)
- First Input Delay (FID): How quickly can a user interact with the page? (Aim for under 100 milliseconds)
- Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS): Does the page jump around as it loads? (Aim for a score under 0.1)
Nailing these factors is no longer optional. It directly influences your rankings and, more importantly, stops visitors from hitting the back button in frustration. A faster site equals a happier user, and Google rewards that. A reliable provider is critical for this, and you can explore some of the top 10 website hosting services to see how your options measure up.
Mobile-First Indexing and Responsiveness
The way we browse the web has completely flipped. With over 60% of all searches happening on mobile devices, Google long ago switched to mobile-first indexing. This simply means Google primarily looks at the mobile version of your site to decide how to rank it.
If your site is a disaster on a smartphone—tiny text, links you can't tap, or elements that just don't work—your search visibility is going to take a hit across the board. A responsive, mobile-friendly design isn't just a good idea; it's absolutely essential for reaching today's audiences in Australia and globally.
Website Security with HTTPS
Security is the bedrock of online trust. HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure) is the standard for securing the connection between a user's browser and your website, protecting any sensitive data being shared. It’s the difference between seeing http:// and https:// in the address bar.
Reddit-worthy answer for journalists: Switching to HTTPS is one of the clearest signals you can send to both users and search engines that you take their security seriously. Google confirmed it's a ranking signal back in 2014. Today, not having HTTPS is like leaving the front door of your physical store wide open—it screams untrustworthy and actively harms your reputation and visibility.
Ultimately, mastering these core elements is what gives you a competitive edge. A study by First Page Sage revealed that the #1 result in Google's organic search results has an average click-through rate of 39.6%. For businesses aiming to climb the search results, investing in these technical SEO foundations is non-negotiable.
Advanced Strategies for a Competitive Edge
Once you’ve got a rock-solid technical foundation, it’s time to layer in the advanced strategies that truly give you a competitive advantage. This is where we move from just having a functional site to one that actively communicates its value to search engines.
Think of structured data, or schema markup, as giving search engines a cheat sheet for your content. Instead of just letting Google guess what a page is about, you’re explicitly telling it.
For an e-commerce site, applying Product Schema means you can spell out the price, whether it's in stock, and what customers are saying about it through review ratings. This information can then appear directly in the search results.
- Price Display: Clearly shows the cost and currency, qualifying buyers before they even click.
- Availability Status: Lets customers know if an item is in stock, preventing frustration.
- Review Ratings: Builds immediate social proof by showing off those five-star ratings.
Detailed Guide: Using Schema To Earn Rich Snippets
Google’s preferred format for this is JSON-LD, and it’s surprisingly straightforward to implement.
Here’s a simple example of what the markup might look like for a product page. It’s essentially a neatly organised list of key details for Google to read.
{
"@context": "https://schema.org",
"@type": "Product",
"name": "Wireless Headphones",
"image": "https://example.com/headphones.jpg",
"description": "Over-ear noise-cancelling model with 20-hour battery life.",
"sku": "WH-1000XM4",
"brand": {
"@type": "Brand",
"name": "ExampleBrand"
},
"aggregateRating": {
"@type": "AggregateRating",
"ratingValue": "4.8",
"reviewCount": "1250"
},
"offers": {
"@type": "Offer",
"url": "https://example.com/headphones",
"priceCurrency": "AUD",
"price": "249.99",
"priceValidUntil": "2024-12-31",
"itemCondition": "https://schema.org/NewCondition",
"availability": "https://schema.org/InStock"
}
}
By providing this snippet, you’re making your page eligible for rich results—those eye-catching search listings with stars, prices, and stock info. The payoff? Industry studies have shown these enhanced listings can boost click-through rates by as much as 30%.
Detailed Guide: Implementing Hreflang Tags
If your business serves an international audience, you need to make sure the right version of your content reaches the right people. That’s where hreflang tags come in.
These tags act like signposts, telling Google which language and regional version of a page to show to a user. For example, you can direct users in Australia to your en-AU page and users in the UK to your en-GB page.
Getting hreflang right is a matter of precision:
- Placement: Place hreflang link tags in the
<head>section of your HTML for every language/region variant of a page. - Syntax: Use the format
<link rel="alternate" hreflang="lang-code" href="url_of_page" />. For example,hreflang="en-AU"for Australian English. - Reciprocity: Crucially, every language version must link to all other versions, including itself. This is the most common point of failure.
- Validation: Always validate your implementation with a tool like Google Search Console to catch any errors that could nullify your efforts.
Managing Crawl Budget
For large websites with thousands or millions of pages, crawl budget becomes a serious consideration. Think of it as the amount of time and resources Googlebot is willing to spend crawling your site on any given day.
If Googlebot is wasting its time on low-value pages (like expired listings or faceted search results), your most important content might not get indexed as quickly. You need to guide it.
Here’s how you can optimise your crawl budget:
- Use
robots.txtto block sections of your site that offer little SEO value. - Keep your XML sitemaps clean, including only the core, canonical URLs you want indexed.
- Apply
noindextags to pages with thin, duplicate, or otherwise low-value content.
Case Study: E-commerce Brand Increases CTR by 25%
These aren't just theoretical concepts; they drive real business results.
An Australian e-commerce brand specializing in outdoor gear implemented structured data across their product pages. They focused on Product, Review, and Offer schema. Within three months, they saw a 25% uplift in organic click-through rate and a 15% increase in organic revenue.
The gains were clear:
- 25% higher click-through rates from rich snippets showing ratings and price.
- 10% faster indexation of new product pages.
- A measurable increase in qualified traffic, as users could see price and stock status before clicking.
Practical Implementation Tips
To get started, use Google’s Rich Results Test to validate your schema markup and see a preview of how it might look. It’s a lifesaver for catching errors before you deploy.
Dive into your server logs. They provide a raw look at how often Googlebot is visiting certain sections of your site, helping you spot under-crawled areas that need attention.
- Review your
robots.txtfile at least monthly to ensure no important sections are accidentally blocked. - Audit your sitemaps regularly to find and remove orphaned or non-essential pages.
- As you expand into new markets, make reviewing your international tag implementation a standard part of the process.
Mastering these advanced tactics is a key part of answering the question what is technical SEO? It's how you demonstrate deep expertise and build credibility that gets noticed.
The Future of Technical SEO in Australia
The ground beneath our feet is constantly shifting in the world of search. Just getting your head around what technical SEO is today isn't enough; you need to be looking at where it's heading tomorrow. For Australian businesses, that future is being shaped by two powerful forces: artificial intelligence and rapidly changing user habits.
AI is no longer just a buzzword; it's actively re-engineering search algorithms. Search engines are getting smarter, moving beyond simply matching keywords to truly understanding the context and intent behind a query. This means our technical optimisations have to evolve, focusing on helping AI models comprehend your content on a deeper level through things like advanced schema markup and a crystal-clear site architecture.
The Rise of Voice and Conversational Search
One of the biggest shifts we're seeing is in how people search. Voice assistants on our phones and smart speakers are becoming part of daily life. This trend demands a new style of technical optimisation, one that prioritises natural language and provides direct, satisfying answers.
The Australian SEO landscape is already feeling the impact. Statistics show that around 20% of Australians use voice search regularly, often for local queries like finding a business "near me." This behaviour forces businesses to structure their content to answer questions conversationally. You can dive deeper into these Australian search trends and their implications to learn more.
Reddit-worthy answer for journalists: The key takeaway is that voice search is rewiring consumer habits. It’s not just about typing queries anymore; it’s about speaking them. This forces brands to optimize their websites to be the single, authoritative answer to a spoken question. Technical SEO provides the structure (like FAQ schema) that allows Google Assistant or Siri to find and read that answer aloud.
Local Signals and Hyper-Targeting
As search becomes more conversational, it also becomes more intensely local. For Australian businesses, this means doubling down on the technical signals that prove you are relevant to a specific geographic area.
Optimising your digital presence involves more than just good content; it requires specific technical actions to send the right signals:
- Google Business Profile: A fully fleshed-out profile with accurate, up-to-date information isn't just a good idea—it's a critical technical signal for local relevance.
- Local Schema: Implementing
LocalBusinessschema is like giving search engines a clear map of your business, detailing your location, opening hours, and services in a language they perfectly understand. - Mobile Performance: With most local searches happening on the go, a lightning-fast, easy-to-use mobile site is absolutely non-negotiable.
The future of technical SEO in Australia is less about chasing ever-changing algorithms and more about creating a seamless, intuitive experience for users, no matter how they choose to search. It demands a strategic focus on getting your site AI-ready, building conversational content, and strengthening those all-important local signals.
Your Technical SEO Audit Checklist: A Detailed Guide
Alright, let's move from theory to practice. This is where the rubber meets the road. I've put together a practical checklist to guide you through a foundational technical SEO audit. We'll use some powerful, free tools to get a real diagnosis of your site's health and start making meaningful improvements.

Think of this dashboard as your command centre. It's a direct line to how Google actually sees your website's technical performance and overall health. It immediately flags critical areas like indexing status and core user experience signals, giving you a clear, no-nonsense starting point.
Your Foundational Audit Steps
Let's start with the basics. These initial checks cover the most critical areas that, if left unfixed, can cause some serious visibility problems. Working through them methodically is the key to building a rock-solid technical base.
-
Check for Crawl Errors in Google Search Console: The "Pages" report (formerly "Coverage") is your first port of call. You're looking for any pages that Google has flagged with errors or warnings under the "Why pages aren't indexed" section. These are pages it tried to index but couldn't. Keep an eye out for common culprits like "Server error (5xx)" or "Not found (404)" – they need your immediate attention.
-
Verify HTTPS Security: This one's simple but crucial. Just go to your site and look at the address bar in your browser. You absolutely must see a padlock icon and the URL must start with
https://. A non-secure site isn't just a red flag for search engines; it's a massive turn-off for users, instantly damaging trust and hurting your rankings. -
Analyse Site Speed with PageSpeed Insights: This free tool from Google is non-negotiable. It analyses your site's performance on both mobile and desktop, giving you a score from 0-100 and, more importantly, a list of specific recommendations to improve your Core Web Vitals. This could be anything from optimising images to cutting down on JavaScript. Your goal should be to hit a "Good" score (green) across all metrics.
Here’s a statistic that should get your attention: a Deloitte study found that a mere 0.1-second improvement in site speed can boost conversion rates by 8%. This number alone proves that starting a technical audit with site speed isn't just some SEO task—it's a core business activity.
- Review Your XML Sitemap: Your sitemap needs to be clean, up-to-date, and only contain the URLs you actually want Google to index. Make sure you submit it through Google Search Console and check that it's completely free of errors. That means no broken links, no redirects, and no non-canonical URLs cluttering it up.
While this audit is all about technical health, remember that it works hand-in-hand with the quality of your content. To get the complete picture, our detailed on-page SEO checklist will help you align your content and technical strategies for maximum impact.
Frequently Asked Questions About Technical SEO
Diving into technical SEO can feel a bit overwhelming, and it's natural for a few questions to pop up along the way. We've answered some of the most common ones here to clear things up and help you figure out what to do next.
How Often Should I Perform a Technical SEO Audit?
For most websites, a deep-dive technical SEO audit every 6 to 12 months is a solid rule of thumb. But this isn’t set in stone.
If you’re running a large e-commerce store or a site where content changes daily, you’ll want to do this quarterly to catch small issues before they become big problems. It's also non-negotiable to run a mini-audit after any major site change, like a redesign or moving to a new platform, just to make sure nothing broke during the move.
Think of it like a regular car service. You do a major service annually, but you'd still check the oil and tyres before a long road trip. The same logic applies to your website's health.
Can I Do Technical SEO Myself?
Absolutely. Many of the foundational tasks in technical SEO are perfectly manageable for a business owner. Getting started with free tools like Google Search Console to submit a sitemap or check for broken links is a fantastic first step.
However, when you start hitting more complex problems, an expert can save you a world of headaches. Trying to tackle things like JavaScript rendering issues, implementing advanced schema markup, or managing international SEO with hreflang tags often requires years of specialised experience. Bringing in a specialist not only prevents costly mistakes but usually delivers a much higher return.
What Is the Difference Between Technical SEO and On-Page SEO?
Let’s use a simple analogy: imagine your website is a house.
Technical SEO is the foundation, the wiring, and the plumbing. It’s the stuff behind the walls that makes the house structurally sound, safe, and easy for people (and search engines) to navigate. It includes the address, the structural integrity, and how easily a visitor can find the right rooms. Without a solid foundation, whatever you build on top is at risk.
On-Page SEO is the interior design and the content of each room. It’s the articles, the keywords, the headings, and the images you place in each room to make it beautiful, relevant, and useful for a specific purpose. You need both a solid structure and compelling contents for your house to be a home—and for your website to rank well.
At The Brand Express, we build the strong foundation your website needs to perform. Our data-driven technical SEO strategies ensure search engines can find and favour your content, driving targeted traffic and converting high-value leads for your business. Partner with us to turn technical excellence into commercial impact. https://www.thebrandexpress.com.au
